A2-word2vec
实验概览
本次作业考察对 word2vec 相关算法的理解,分为两部分,第一部分是计算题,第二部分为代码
Part 1: Understanding word2vec
知识回顾
设中心单词为
所有单词的上下文向量组成矩阵
最后的输出
题目

Answer:因为

Answer:
求偏导:

Answer:
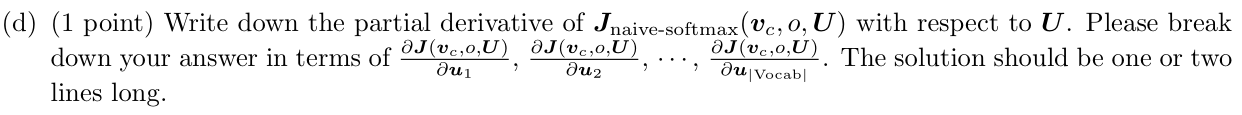
Answer:

Answer:

Answer:

Answer:

Answer:

Answer:
Part 2: Implementing word2vec
实现 sigmoid 函数
很简单,不必多说:
def sigmoid(x):
"""
Compute the sigmoid function for the input here.
Arguments:
x -- A scalar or numpy array.
Return:
s -- sigmoid(x)
"""
### YOUR CODE HERE (~1 Line)
s = 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
### END YOUR CODE
return s
实现 softmax 函数
老师已经为我们实现了 softmax,写法非常精彩,于是把代码拿出来赏析一下
softmax 函数为:
由于指数运算,这样会有溢出的风险,注意到:
于是就可以对每一个向量运算时,先减去其最大值,代码如下:
def softmax(x):
"""Compute the softmax function for each row of the input x.
It is crucial that this function is optimized for speed because
it will be used frequently in later code.
Arguments:
x -- A D dimensional vector or N x D dimensional numpy matrix.
Return:
x -- You are allowed to modify x in-place
"""
orig_shape = x.shape
if len(x.shape) > 1:
# Matrix
tmp = np.max(x, axis=1)
x -= tmp.reshape((x.shape[0], 1))
x = np.exp(x)
tmp = np.sum(x, axis=1)
x /= tmp.reshape((x.shape[0], 1))
else:
# Vector
tmp = np.max(x)
x -= tmp
x = np.exp(x)
tmp = np.sum(x)
x /= tmp
assert x.shape == orig_shape
return x
实现计算损失函数及梯度
根据第一部分的公式推导计算即可,注意维度的关系
def naiveSoftmaxLossAndGradient(
centerWordVec,
outsideWordIdx,
outsideVectors,
dataset
):
""" Naive Softmax loss & gradient function for word2vec models
Implement the naive softmax loss and gradients between a center word's
embedding and an outside word's embedding. This will be the building block
for our word2vec models. For those unfamiliar with numpy notation, note
that a numpy ndarray with a shape of (x, ) is a one-dimensional array, which
you can effectively treat as a vector with length x.
Arguments:
centerWordVec -- numpy ndarray, center word's embedding
in shape (word vector length, )
(v_c in the pdf handout)
outsideWordIdx -- integer, the index of the outside word
(o of u_o in the pdf handout)
outsideVectors -- outside vectors is
in shape (num words in vocab, word vector length)
for all words in vocab (tranpose of U in the pdf handout)
dataset -- needed for negative sampling, unused here.
Return:
loss -- naive softmax loss
gradCenterVec -- the gradient with respect to the center word vector
in shape (word vector length, )
(dJ / dv_c in the pdf handout)
gradOutsideVecs -- the gradient with respect to all the outside word vectors
in shape (num words in vocab, word vector length)
(dJ / dU)
"""
### YOUR CODE HERE (~6-8 Lines)
### Please use the provided softmax function (imported earlier in this file)
### This numerically stable implementation helps you avoid issues pertaining
### to integer overflow.
centerWordVec = centerWordVec.reshape(centerWordVec.shape[0], 1)
y = softmax(np.dot(outsideVectors, centerWordVec).reshape(-1)).reshape(-1, 1) # (num, 1)
loss = -np.log(y[outsideWordIdx])
y[outsideWordIdx] -= 1
gradCenterVec = np.dot(outsideVectors.T, y) # (word vector, num)
gradOutsideVecs = np.dot(y, centerWordVec.T) # (num, word vector)
### END YOUR CODE
return loss, gradCenterVec, gradOutsideVecs
实现负采样的损失函数及梯度
还是依据上述公式写即可,注意
def negSamplingLossAndGradient(
centerWordVec,
outsideWordIdx,
outsideVectors,
dataset,
K=10
):
""" Negative sampling loss function for word2vec models
Implement the negative sampling loss and gradients for a centerWordVec
and a outsideWordIdx word vector as a building block for word2vec
models. K is the number of negative samples to take.
Note: The same word may be negatively sampled multiple times. For
example if an outside word is sampled twice, you shall have to
double count the gradient with respect to this word. Thrice if
it was sampled three times, and so forth.
Arguments/Return Specifications: same as naiveSoftmaxLossAndGradient
"""
# Negative sampling of words is done for you. Do not modify this if you
# wish to match the autograder and receive points!
negSampleWordIndices = getNegativeSamples(outsideWordIdx, dataset, K)
indices = [outsideWordIdx] + negSampleWordIndices
### YOUR CODE HERE (~10 Lines)
z = sigmoid(np.dot(outsideVectors[negSampleWordIndices], centerWordVec)) # sum v_cv_k
b = sigmoid(np.dot(outsideVectors[outsideWordIdx], centerWordVec)) # v_ov_C
loss = -np.log(b) - np.sum(np.log(1 - z))
gradCenterVec = (b - 1) * outsideVectors[outsideWordIdx] + np.sum(z.reshape(-1, 1) * outsideVectors[negSampleWordIndices],axis=0)
gradOutsideVecs = np.zeros_like(outsideVectors)
gradOutsideVecs[outsideWordIdx] = (b - 1) * centerWordVec
for j, index in enumerate(negSampleWordIndices):
gradOutsideVecs[index] += z[j] * centerWordVec
### Please use your implementation of sigmoid in here.
### END YOUR CODE
return loss, gradCenterVec, gradOutsideVecs
实现 skip-gram 算法
调用前面实现的负采样函数,计算损失值和梯度即可
def skipgram(currentCenterWord, windowSize, outsideWords, word2Ind,
centerWordVectors, outsideVectors, dataset,
word2vecLossAndGradient=naiveSoftmaxLossAndGradient):
""" Skip-gram model in word2vec
Implement the skip-gram model in this function.
Arguments:
currentCenterWord -- a string of the current center word
windowSize -- integer, context window size
outsideWords -- list of no more than 2*windowSize strings, the outside words
word2Ind -- a dictionary that maps words to their indices in
the word vector list
centerWordVectors -- center word vectors (as rows) is in shape
(num words in vocab, word vector length)
for all words in vocab (V in pdf handout)
outsideVectors -- outside vectors is in shape
(num words in vocab, word vector length)
for all words in vocab (transpose of U in the pdf handout)
word2vecLossAndGradient -- the loss and gradient function for
a prediction vector given the outsideWordIdx
word vectors, could be one of the two
loss functions you implemented above.
Return:
loss -- the loss function value for the skip-gram model
(J in the pdf handout)
gradCenterVec -- the gradient with respect to the center word vector
in shape (num words in vocab, word vector length)
(dJ / dv_c in the pdf handout)
gradOutsideVecs -- the gradient with respect to all the outside word vectors
in shape (num words in vocab, word vector length)
(dJ / dU)
"""
loss = 0.0
gradCenterVecs = np.zeros(centerWordVectors.shape)
gradOutsideVectors = np.zeros(outsideVectors.shape)
### YOUR CODE HERE (~8 Lines)
currentCenterWordIdx=word2Ind[currentCenterWord]
currentCenterWordVec=centerWordVectors[currentCenterWordIdx]
for outsideWord in outsideWords:
(curloss,curgradCenterVecs,curgradOutVecs)=word2vecLossAndGradient(currentCenterWordVec,
word2Ind[outsideWord],
outsideVectors,
dataset)
loss += curloss
gradCenterVecs[currentCenterWordIdx] += curgradCenterVecs.flatten()
gradOutsideVectors += curgradOutVecs
### END YOUR CODE
return loss, gradCenterVecs, gradOutsideVectors
实现随机梯度下降算法
根据函数的梯度更新即可
def sgd(f, x0, step, iterations, postprocessing=None, useSaved=False,
PRINT_EVERY=10):
""" Stochastic Gradient Descent
Implement the stochastic gradient descent method in this function.
Arguments:
f -- the function to optimize, it should take a single
argument and yield two outputs, a loss and the gradient
with respect to the arguments
x0 -- the initial point to start SGD from
step -- the step size for SGD
iterations -- total iterations to run SGD for
postprocessing -- postprocessing function for the parameters
if necessary. In the case of word2vec we will need to
normalize the word vectors to have unit length.
PRINT_EVERY -- specifies how many iterations to output loss
Return:
x -- the parameter value after SGD finishes
"""
# Anneal learning rate every several iterations
ANNEAL_EVERY = 20000
if useSaved:
start_iter, oldx, state = load_saved_params()
if start_iter > 0:
x0 = oldx
step *= 0.5 ** (start_iter / ANNEAL_EVERY)
if state:
random.setstate(state)
else:
start_iter = 0
x = x0
if not postprocessing:
postprocessing = lambda x: x
exploss = None
for iter in range(start_iter + 1, iterations + 1):
# You might want to print the progress every few iterations.
loss = None
### YOUR CODE HERE (~2 lines)
loss, grad = f(x)
x -= step * grad
### END YOUR CODE
x = postprocessing(x)
if iter % PRINT_EVERY == 0:
if not exploss:
exploss = loss
else:
exploss = .95 * exploss + .05 * loss
print("iter %d: %f" % (iter, exploss))
if iter % SAVE_PARAMS_EVERY == 0 and useSaved:
save_params(iter, x)
if iter % ANNEAL_EVERY == 0:
step *= 0.5
return x
运行
回顾一下整个框架:
- 模型采用 skip-gram,根据中心词向量计算上下文词向量,由此得到损失函数
- 计算损失函数和梯度时使用负采样方法,从而提高模型效率
- 最后更新参数时使用随机梯度下降法
以上我们就搭建好了整个 word2vec 模型!
对斯坦福提供的数据集迭代计算 40000 次:
wordVectors = sgd(
lambda vec: word2vec_sgd_wrapper(skipgram, tokens, vec, dataset, C,
negSamplingLossAndGradient),
wordVectors, 0.3, 40000, None, True, PRINT_EVERY=10)
跑了将近一个小时,终于出来结果了:

这是一些训练后的词向量的可视化:

可以看到:
- 同义词以及词性相同的反义词非常靠近,如 wonderful,amazing,great,boring。这很容易理解
- 像 queen 和 king 形成的向量与 female 和 male 形成的向量基本平行