A4-NMT with RNNs
本次作业是实现一个机器翻译模型 NMT with RNNs,该模型是一个典型的 Encoder-Decoder 架构,它的架构图如下:

为了便于理解和编写代码,我在原图基础上补充了一些细节:

模型架构
下面对每个模块进行单独说明
Encoder
该部分对应图中圈出区域:

对于源语言的一个句子,先得到它的词嵌入矩阵:
接下来将矩阵放入一个双向 LSTM 中,由于是双向 LSTM,所以每一个 hidden state 和 cell state 都由正向和反向两个方向拼接而成:
由此加入一个 Linear 层初始化 decoder 的第一个 hidden state 和 cell state:
Decoder

当 Decoder 的参数初始化后,我就需要输入目标语言了,在第
Attention

接下来,使用
计算输出

接下来将
接下来即可得到词概率向量:
损失函数设置为
搜索策略
得到概率向量后,怎么选择当前词呢,这是一个策略问题
Greedy decoding
得到概率向量后,一个很自然的想法就是每步选取概率最大的词作为输出即可。但是这种做法并不妥,它一旦选错一个词,那么后续生成的内容很有可能也会出错,比如下面的例子:

按尝时来讲,当输出 "he hit" 后,下一步输出的概率最大的词很有可能是 "a",但是一旦选中 "a",后续的翻译就不好进行了。
Exhaustive search decoding
想法是最大化下面这个值:

那么就需要计算所有可能的 y 序列,设词汇表大小为
Beam search decoding
将前两种方法折中,我们就得到了一种新的方法 beam search,它即计算了多种可能性,时间复杂度也没有过高。
具体做法是每次都选取概率最大的

我们要做的就是寻找分数最高的序列。

注意,最后的分数都是负数。
那么搜索什么时候停止呢?
- 在 greedy decoding 中,我们总是在输出
<END>时停止 - 但是在 beam search 中,不同的序列可能不会同时输出
<END>,我们可以设置一个时间节点,到达时停止,或者在有 个序列输出 <END>时停止。
还有一个问题是序列越长的句子,它的概率乘积肯定越小,这是不公平的,解决办法是用序列长度正则化:

代码实现
代码架构
整个项目有 4 个部分,utils.py,vacab.py,model_embeddings.py 和 nmt_model.py
utils.py
pad_sents将一个 batch 中的句子补齐read_corpus读入数据集,并且将每个目标语言数据集的句首加上<s>,句尾加上</s>batch_iter将句子打乱,生成 batch
vacab.py
这一部分主要是用来构建单词表
class VocabEntry(object):
def __init__(self, word2id=None): # 将单词和索引对应起来
def __getitem__(self, word): # 得到对应单词的索引
def __contains__(self, word):# 查看单词是否存在单词表中
def __len__(self): #单词表大小
def id2word(self, wid): # 根据索引找到单词
def add(self, word): # 将单词添加到单词表末尾
def words2indices(self, sents): # 将一个句子转换为索引
def indices2words(self, word_ids): # 将一列索引转换为句子
def to_input_tensor(self, sents: List[List[str]], device: torch.device) -> torch.Tensor: # 将一个句子转为tensor
def from_corpus(corpus, size, freq_cutoff=2): # 根据一整个语料库直接构建单词表
def from_subword_list(subword_list):
class Vocab(object):
def __init__(self, src_vocab: VocabEntry, tgt_vocab: VocabEntry):
def build(src_sents, tgt_sents) -> 'Vocab': # 构建单词表
def save(self, file_path): # 将单词表存到本地
def load(file_path): # 从本地读取单词表
model_embeddings.py
为词表初始化词向量
nmt_model.py
实现 NMT 模型
class NMT(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, embed_size, hidden_size, vocab, dropout_rate=0.2):#初始化模型需要的各个层
def forward(self, source: List[List[str]], target: List[List[str]]) -> torch.Tensor:#前向传播过程,根据源语言句子和目标语言句子,通过encode,decode生成句子的对数概率
def encode(self, source_padded: torch.Tensor, source_lengths: List[int]) -> Tuple[torch.Tensor, Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]]:#encode模块,后面会讲到
def decode(self, enc_hiddens: torch.Tensor, enc_masks: torch.Tensor, dec_init_state: Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor], target_padded: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:#decode模块,后面会讲到
def step(self, Ybar_t: torch.Tensor,dec_state: Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor],enc_hiddens: torch.Tensor,enc_hiddens_proj: torch.Tensor, enc_masks: torch.Tensor) -> Tuple[Tuple, torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]:#训练时,每一个t时,decode的更新
def beam_search(self, src_sent: List[str], beam_size: int=5, max_decoding_time_step: int=70) -> List[Hypothesis]:#前面讲到的搜索策略
def load(model_path: str):#从本地加载模型
def save(self, path: str):#把模型保存到本地
初始化词向量实现
为了便于操作,我们需要把每一个 batch 的句子长度对齐,方法是得到 batch 中最长的句子长度,其它句子补上 pad_token
def pad_sents(sents, pad_token):
""" Pad list of sentences according to the longest sentence in the batch.
The paddings should be at the end of each sentence.
@param sents (list[list[str]]): list of sentences, where each sentence
is represented as a list of words
@param pad_token (str): padding token
@returns sents_padded (list[list[str]]): list of sentences where sentences shorter
than the max length sentence are padded out with the pad_token, such that
each sentences in the batch now has equal length.
"""
sents_padded = []
### YOUR CODE HERE (~6 Lines)
max_len = max([len(str) for str in sents])
for str in sents:
sents_padded.append(str + (max_len - len(str)) * [pad_token])
### END YOUR CODE
return sents_padded
然后利用 torch.nn.Embedding 就可以初始化词向量了:
def __init__(self, embed_size, vocab):
"""
Init the Embedding layers.
@param embed_size (int): Embedding size (dimensionality)
@param vocab (Vocab): Vocabulary object containing src and tgt languages
See vocab.py for documentation.
"""
super(ModelEmbeddings, self).__init__()
self.embed_size = embed_size
# default values
self.source = None
self.target = None
src_pad_token_idx = vocab.src['<pad>']
tgt_pad_token_idx = vocab.tgt['<pad>']
### YOUR CODE HERE (~2 Lines)
### TODO - Initialize the following variables:
### self.source (Embedding Layer for source language)
### self.target (Embedding Layer for target langauge)
###
### Note:
### 1. `vocab` object contains two vocabularies:
### `vocab.src` for source
### `vocab.tgt` for target
### 2. You can get the length of a specific vocabulary by running:
### `len(vocab.<specific_vocabulary>)`
### 3. Remember to include the padding token for the specific vocabulary
### when creating your Embedding.
###
### Use the following docs to properly initialize these variables:
### Embedding Layer:
### https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/nn.html#torch.nn.Embedding
self.source = nn.Embedding(len(vocab.src), embed_size, padding_idx=src_pad_token_idx)
self.target = nn.Embedding(len(vocab.tgt), embed_size, padding_idx=tgt_pad_token_idx)
### END YOUR CODE
初始化模型 layers
根据我们前一部分对模型每一块的分析,把握住每一层输入和输出的维度,这一步很容易就能实现:
def __init__(self, embed_size, hidden_size, vocab, dropout_rate=0.2):
""" Init NMT Model.
@param embed_size (int): Embedding size (dimensionality)
@param hidden_size (int): Hidden Size, the size of hidden states (dimensionality)
@param vocab (Vocab): Vocabulary object containing src and tgt languages
See vocab.py for documentation.
@param dropout_rate (float): Dropout probability, for attention
"""
super(NMT, self).__init__()
self.model_embeddings = ModelEmbeddings(embed_size, vocab)
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.dropout_rate = dropout_rate
self.vocab = vocab
# default values
self.encoder = None
self.decoder = None
self.h_projection = None
self.c_projection = None
self.att_projection = None
self.combined_output_projection = None
self.target_vocab_projection = None
self.dropout = None
# For sanity check only, not relevant to implementation
self.gen_sanity_check = False
self.counter = 0
### YOUR CODE HERE (~8 Lines)
### TODO - Initialize the following variables:
### self.encoder (Bidirectional LSTM with bias)
### self.decoder (LSTM Cell with bias)
### self.h_projection (Linear Layer with no bias), called W_{h} in the PDF.
### self.c_projection (Linear Layer with no bias), called W_{c} in the PDF.
### self.att_projection (Linear Layer with no bias), called W_{attProj} in the PDF.
### self.combined_output_projection (Linear Layer with no bias), called W_{u} in the PDF.
### self.target_vocab_projection (Linear Layer with no bias), called W_{vocab} in the PDF.
### self.dropout (Dropout Layer)
###
### Use the following docs to properly initialize these variables:
### LSTM:
### https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/nn.html#torch.nn.LSTM
### LSTM Cell:
### https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/nn.html#torch.nn.LSTMCell
### Linear Layer:
### https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/nn.html#torch.nn.Linear
### Dropout Layer:
### https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/nn.html#torch.nn.Dropout
self.encoder = nn.LSTM(input_size=embed_size, hidden_size=hidden_size, bias=True, bidirectional=True)
# 前一个 h/c 和当前 y
self.decoder = nn.LSTMCell(input_size=embed_size+hidden_size, hidden_size=hidden_size, bias=True)
# concat(h_1, h_m)
self.h_projection = nn.Linear(self.hidden_size*2, self.hidden_size, bias=False)
# concat(c_1, c_m)
self.c_projection = nn.Linear(self.hidden_size*2, self.hidden_size, bias=False)
# h_t dec
self.att_projection = nn.Linear(self.hidden_size*2, self.hidden_size, bias=False)
# a_t : h, h_t : 2 h
self.combined_output_projection = nn.Linear(self.hidden_size*3, self.hidden_size, bias=False)
# v_t
self.target_vocab_projection = nn.Linear(self.hidden_size, len(self.vocab.tgt), bias=False)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(p=self.dropout_rate, inplace=False)
### END YOUR CODE
实现 encode
代码如下:
这个函数需要返回 Encoder 部分的 state 和初始化 Decoder 的第一个 state
def encode(self, source_padded: torch.Tensor, source_lengths: List[int]) -> Tuple[torch.Tensor, Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]]:
""" Apply the encoder to source sentences to obtain encoder hidden states.
Additionally, take the final states of the encoder and project them to obtain initial states for decoder.
@param source_padded (Tensor): Tensor of padded source sentences with shape (src_len, b), where
b = batch_size, src_len = maximum source sentence length. Note that
these have already been sorted in order of longest to shortest sentence.
@param source_lengths (List[int]): List of actual lengths for each of the source sentences in the batch
@returns enc_hiddens (Tensor): Tensor of hidden units with shape (b, src_len, h*2), where
b = batch size, src_len = maximum source sentence length, h = hidden size.
@returns dec_init_state (tuple(Tensor, Tensor)): Tuple of tensors representing the decoder's initial
hidden state and cell.
"""
enc_hiddens, dec_init_state = None, None
### YOUR CODE HERE (~ 8 Lines)
### TODO:
### 1. Construct Tensor `X` of source sentences with shape (src_len, b, e) using the source model embeddings.
### src_len = maximum source sentence length, b = batch size, e = embedding size. Note
### that there is no initial hidden state or cell for the decoder.
### 2. Compute `enc_hiddens`, `last_hidden`, `last_cell` by applying the encoder to `X`.
### - Before you can apply the encoder, you need to apply the `pack_padded_sequence` function to X.
### - After you apply the encoder, you need to apply the `pad_packed_sequence` function to enc_hiddens.
### - Note that the shape of the tensor returned by the encoder is (src_len, b, h*2) and we want to
### return a tensor of shape (b, src_len, h*2) as `enc_hiddens`.
### 3. Compute `dec_init_state` = (init_decoder_hidden, init_decoder_cell):
### - `init_decoder_hidden`:
### `last_hidden` is a tensor shape (2, b, h). The first dimension corresponds to forwards and backwards.
### Concatenate the forwards and backwards tensors to obtain a tensor shape (b, 2*h).
### Apply the h_projection layer to this in order to compute init_decoder_hidden.
### This is h_0^{dec} in the PDF. Here b = batch size, h = hidden size
### - `init_decoder_cell`:
### `last_cell` is a tensor shape (2, b, h). The first dimension corresponds to forwards and backwards.
### Concatenate the forwards and backwards tensors to obtain a tensor shape (b, 2*h).
### Apply the c_projection layer to this in order to compute init_decoder_cell.
### This is c_0^{dec} in the PDF. Here b = batch size, h = hidden size
###
### See the following docs, as you may need to use some of the following functions in your implementation:
### Pack the padded sequence X before passing to the encoder:
### https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/nn.html#torch.nn.utils.rnn.pack_padded_sequence
### Pad the packed sequence, enc_hiddens, returned by the encoder:
### https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/nn.html#torch.nn.utils.rnn.pad_packed_sequence
### Tensor Concatenation:
### https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/torch.html#torch.cat
### Tensor Permute:
### https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/tensors.html#torch.Tensor.permute
X = self.model_embeddings.source(source_padded)
X_packed = pack_padded_sequence(X, torch.tensor(source_lengths))
enc_hiddens, (last_hidden, last_cell) = self.encoder(X_packed)
enc_hiddens, _ = pad_packed_sequence(enc_hiddens, batch_first=True)
# last_hidden 包含了正向和反向的 h, (2, b, h)
init_decoder_hidden = self.h_projection(torch.cat((last_hidden[0], last_hidden[1]), 1))
init_decoder_cell = self.c_projection(torch.cat((last_cell[0], last_cell[1]), 1))
dec_init_state = (init_decoder_hidden, init_decoder_cell)
### END YOUR CODE
return enc_hiddens, dec_init_state
注意 torch.nn.LSTM() 的返回值:

当设置为双向 LSTM 时,
这里还使用到了 pack_padded_sequence 和 pad_packed_sequence 操作。下面讲解以下这两步操作的作用。
在代码实现的第一部分,我们将长短不一的句子用 pad_token 补齐,然后在调用 nn.Embedding 时,将这些位置输入了进去,那么最后产生的词向量在 pad_token 位置的值均为 0。如果在进行 forward 计算时,把 pad_token 也考虑进去,可能会导致 RNN 计算了了很多无用的 pad_token,这样不仅浪费计算资源,最后得到的值可能还会存在误差。所以 pack_padded_sequence 的作用就是压缩,将这些填充值去除。
那么显然,pad_packed_sequence 就是将压缩后的值再恢复原貌,进行后面的计算。
实现 decode
首先实现根据当前的 encoder state 和当前的 decoder state 计算新的 decoder state,然后算出 attention scores 最终得到输出
代码如下:
def step(self, Ybar_t: torch.Tensor,
dec_state: Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor],
enc_hiddens: torch.Tensor,
enc_hiddens_proj: torch.Tensor,
enc_masks: torch.Tensor) -> Tuple[Tuple, torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]:
""" Compute one forward step of the LSTM decoder, including the attention computation.
@param Ybar_t (Tensor): Concatenated Tensor of [Y_t o_prev], with shape (b, e + h). The input for the decoder,
where b = batch size, e = embedding size, h = hidden size.
@param dec_state (tuple(Tensor, Tensor)): Tuple of tensors both with shape (b, h), where b = batch size, h = hidden size.
First tensor is decoder's prev hidden state, second tensor is decoder's prev cell.
@param enc_hiddens (Tensor): Encoder hidden states Tensor, with shape (b, src_len, h * 2), where b = batch size,
src_len = maximum source length, h = hidden size.
@param enc_hiddens_proj (Tensor): Encoder hidden states Tensor, projected from (h * 2) to h. Tensor is with shape (b, src_len, h),
where b = batch size, src_len = maximum source length, h = hidden size.
@param enc_masks (Tensor): Tensor of sentence masks shape (b, src_len),
where b = batch size, src_len is maximum source length.
@returns dec_state (tuple (Tensor, Tensor)): Tuple of tensors both shape (b, h), where b = batch size, h = hidden size.
First tensor is decoder's new hidden state, second tensor is decoder's new cell.
@returns combined_output (Tensor): Combined output Tensor at timestep t, shape (b, h), where b = batch size, h = hidden size.
@returns e_t (Tensor): Tensor of shape (b, src_len). It is attention scores distribution.
Note: You will not use this outside of this function.
We are simply returning this value so that we can sanity check
your implementation.
"""
combined_output = None
### YOUR CODE HERE (~3 Lines)
### TODO:
### 1. Apply the decoder to `Ybar_t` and `dec_state`to obtain the new dec_state.
### 2. Split dec_state into its two parts (dec_hidden, dec_cell)
### 3. Compute the attention scores e_t, a Tensor shape (b, src_len).
### Note: b = batch_size, src_len = maximum source length, h = hidden size.
###
### Hints:
### - dec_hidden is shape (b, h) and corresponds to h^dec_t in the PDF (batched)
### - enc_hiddens_proj is shape (b, src_len, h) and corresponds to W_{attProj} h^enc (batched).
### - Use batched matrix multiplication (torch.bmm) to compute e_t (be careful about the input/ output shapes!)
### - To get the tensors into the right shapes for bmm, you will need to do some squeezing and unsqueezing.
### - When using the squeeze() function make sure to specify the dimension you want to squeeze
### over. Otherwise, you will remove the batch dimension accidentally, if batch_size = 1.
###
### Use the following docs to implement this functionality:
### Batch Multiplication:
### https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/torch.html#torch.bmm
### Tensor Unsqueeze:
### https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/torch.html#torch.unsqueeze
### Tensor Squeeze:
### https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/torch.html#torch.squeeze
(dec_hidden, dec_cell) = self.decoder(Ybar_t, dec_state)
dec_state = (dec_hidden, dec_cell)
# enc_hiddens_proj: (b, src_len, h)
# dec_hidden: (b, h) -> (b, h, 1)
e_t = torch.bmm(enc_hiddens_proj, dec_hidden.unsqueeze(2)).squeeze(2)
# (b, src_len)
### END YOUR CODE
# Set e_t to -inf where enc_masks has 1
if enc_masks is not None:
e_t.data.masked_fill_(enc_masks.bool(), -float('inf'))
### YOUR CODE HERE (~6 Lines)
### TODO:
### 1. Apply softmax to e_t to yield alpha_t
### 2. Use batched matrix multiplication between alpha_t and enc_hiddens to obtain the
### attention output vector, a_t.
#$$ Hints:
### - alpha_t is shape (b, src_len)
### - enc_hiddens is shape (b, src_len, 2h)
### - a_t should be shape (b, 2h)
### - You will need to do some squeezing and unsqueezing.
### Note: b = batch size, src_len = maximum source length, h = hidden size.
###
### 3. Concatenate dec_hidden with a_t to compute tensor U_t
### 4. Apply the combined output projection layer to U_t to compute tensor V_t
### 5. Compute tensor O_t by first applying the Tanh function and then the dropout layer.
###
### Use the following docs to implement this functionality:
### Softmax:
### https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/nn.functional.html#torch.nn.functional.softmax
### Batch Multiplication:
### https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/torch.html#torch.bmm
### Tensor View:
### https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/tensors.html#torch.Tensor.view
### Tensor Concatenation:
### https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/torch.html#torch.cat
### Tanh:
### https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/torch.html#torch.tanh
alpha_t = F.softmax(e_t, dim=1)
# alpha_t : (b, src_len) -> (b, 1, src_len)
# enc_hiddens: (b, src_len, 2h)
a_t = torch.bmm(alpha_t.unsqueeze(1), enc_hiddens).squeeze(1)
U_t = torch.cat((a_t, dec_hidden), dim=1)
V_t = self.combined_output_projection(U_t)
O_t = self.dropout(torch.tanh(V_t))
### END YOUR CODE
combined_output = O_t
return dec_state, combined_output, e_t
然后 decode 从左往右按时序不断调用 step 函数,将每一步输出
def decode(self, enc_hiddens: torch.Tensor, enc_masks: torch.Tensor,
dec_init_state: Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor], target_padded: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
"""Compute combined output vectors for a batch.
@param enc_hiddens (Tensor): Hidden states (b, src_len, h*2), where
b = batch size, src_len = maximum source sentence length, h = hidden size.
@param enc_masks (Tensor): Tensor of sentence masks (b, src_len), where
b = batch size, src_len = maximum source sentence length.
@param dec_init_state (tuple(Tensor, Tensor)): Initial state and cell for decoder
@param target_padded (Tensor): Gold-standard padded target sentences (tgt_len, b), where
tgt_len = maximum target sentence length, b = batch size.
@returns combined_outputs (Tensor): combined output tensor (tgt_len, b, h), where
tgt_len = maximum target sentence length, b = batch_size, h = hidden size
"""
# Chop off the <END> token for max length sentences.
target_padded = target_padded[:-1]
# Initialize the decoder state (hidden and cell)
dec_state = dec_init_state
# Initialize previous combined output vector o_{t-1} as zero
batch_size = enc_hiddens.size(0)
o_prev = torch.zeros(batch_size, self.hidden_size, device=self.device)
# Initialize a list we will use to collect the combined output o_t on each step
combined_outputs = []
### YOUR CODE HERE (~9 Lines)
### TODO:
### 1. Apply the attention projection layer to `enc_hiddens` to obtain `enc_hiddens_proj`,
### which should be shape (b, src_len, h),
### where b = batch size, src_len = maximum source length, h = hidden size.
### This is applying W_{attProj} to h^enc, as described in the PDF.
### 2. Construct tensor `Y` of target sentences with shape (tgt_len, b, e) using the target model embeddings.
### where tgt_len = maximum target sentence length, b = batch size, e = embedding size.
### 3. Use the torch.split function to iterate over the time dimension of Y.
### Within the loop, this will give you Y_t of shape (1, b, e) where b = batch size, e = embedding size.
### - Squeeze Y_t into a tensor of dimension (b, e).
### - Construct Ybar_t by concatenating Y_t with o_prev on their last dimension
### - Use the step function to compute the the Decoder's next (cell, state) values
### as well as the new combined output o_t.
### - Append o_t to combined_outputs
### - Update o_prev to the new o_t.
### 4. Use torch.stack to convert combined_outputs from a list length tgt_len of
### tensors shape (b, h), to a single tensor shape (tgt_len, b, h)
### where tgt_len = maximum target sentence length, b = batch size, h = hidden size.
###
### Note:
### - When using the squeeze() function make sure to specify the dimension you want to squeeze
### over. Otherwise, you will remove the batch dimension accidentally, if batch_size = 1.
###
### You may find some of these functions useful:
### Zeros Tensor:
### https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/torch.html#torch.zeros
### Tensor Splitting (iteration):
### https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/torch.html#torch.split
### Tensor Dimension Squeezing:
### https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/torch.html#torch.squeeze
### Tensor Concatenation:
### https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/torch.html#torch.cat
### Tensor Stacking:
### https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/torch.html#torch.stack
enc_hiddens_proj = self.att_projection(enc_hiddens)
Y = self.model_embeddings.target(target_padded)
Y = torch.split(Y, 1, dim=0)
for Y_t in Y:
# Y_t : (1, b, e)
Y_t = Y_t.squeeze()
# Y_t : (b, e)
Ybar_t = torch.cat((Y_t, o_prev), 1)
dec_state, o_t, e_t = self.step(Ybar_t, dec_state, enc_hiddens, enc_hiddens_proj, enc_masks)
combined_outputs.append(o_t)
o_prev = o_t
combined_outputs = torch.stack(combined_outputs, dim=0)
### END YOUR CODE
return combined_outputs
顺着前面讲解的架构写即可,上述两个函数要注意的问题:
- 为了实现对每一个 batch 的矩阵乘法,可以使用
torch.bmm函数计算 - 代码实现中要注意维度关系,适时使用
torch.squeeze和torch.unsqueeze
Beam Search
代码及注释如下:
def beam_search(self, src_sent: List[str], beam_size: int=5, max_decoding_time_step: int=70) -> List[Hypothesis]:
""" Given a single source sentence, perform beam search, yielding translations in the target language.
@param src_sent (List[str]): a single source sentence (words)
@param beam_size (int): beam size
@param max_decoding_time_step (int): maximum number of time steps to unroll the decoding RNN
@returns hypotheses (List[Hypothesis]): a list of hypothesis, each hypothesis has two fields:
value: List[str]: the decoded target sentence, represented as a list of words
score: float: the log-likelihood of the target sentence
"""
src_sents_var = self.vocab.src.to_input_tensor([src_sent], self.device)
src_encodings, dec_init_vec = self.encode(src_sents_var, [len(src_sent)])
src_encodings_att_linear = self.att_projection(src_encodings)
h_tm1 = dec_init_vec
att_tm1 = torch.zeros(1, self.hidden_size, device=self.device)
eos_id = self.vocab.tgt['</s>']
# 保存当前层的每个序列
hypotheses = [['<s>']]
# 当前层每个序列的分数
hyp_scores = torch.zeros(len(hypotheses), dtype=torch.float, device=self.device)
# 终止的序列
completed_hypotheses = []
t = 0
while len(completed_hypotheses) < beam_size and t < max_decoding_time_step:
t += 1
# 当前序列数量
hyp_num = len(hypotheses)
# 对当前每一个词,都扩展一份enc,方便后续运算
# src_encodings : (1, src_len, h * 2)->(hyp_num, src_len, h * 2)
exp_src_encodings = src_encodings.expand(hyp_num,
src_encodings.size(1),
src_encodings.size(2))
exp_src_encodings_att_linear = src_encodings_att_linear.expand(hyp_num,
src_encodings_att_linear.size(1),
src_encodings_att_linear.size(2))
# 每个序列的最后一个词合起来进行预测
y_tm1 = torch.tensor([self.vocab.tgt[hyp[-1]] for hyp in hypotheses], dtype=torch.long, device=self.device)
y_t_embed = self.model_embeddings.target(y_tm1)
x = torch.cat([y_t_embed, att_tm1], dim=-1)
(h_t, cell_t), att_t, _ = self.step(x, h_tm1,
exp_src_encodings, exp_src_encodings_att_linear, enc_masks=None)
# log probabilities over target words
# 得到每个词概率
log_p_t = F.log_softmax(self.target_vocab_projection(att_t), dim=-1)
# 待搜索的序列数量
live_hyp_num = beam_size - len(completed_hypotheses)
# 对于每一个序列,计算分数
contiuating_hyp_scores = (hyp_scores.unsqueeze(1).expand_as(log_p_t) + log_p_t).view(-1)
# 找到 k 个概率最高的序列
top_cand_hyp_scores, top_cand_hyp_pos = torch.topk(contiuating_hyp_scores, k=live_hyp_num)
# 序列的索引
prev_hyp_ids = torch.div(top_cand_hyp_pos, len(self.vocab.tgt), rounding_mode='floor')
# 当前词
hyp_word_ids = top_cand_hyp_pos % len(self.vocab.tgt)
new_hypotheses = []
live_hyp_ids = []
new_hyp_scores = []
for prev_hyp_id, hyp_word_id, cand_new_hyp_score in zip(prev_hyp_ids, hyp_word_ids, top_cand_hyp_scores):
prev_hyp_id = prev_hyp_id.item()
hyp_word_id = hyp_word_id.item()
cand_new_hyp_score = cand_new_hyp_score.item()
hyp_word = self.vocab.tgt.id2word[hyp_word_id]
new_hyp_sent = hypotheses[prev_hyp_id] + [hyp_word]
# 当前序列搜索完成, 加入completed_hypotheses中
if hyp_word == '</s>':
completed_hypotheses.append(Hypothesis(value=new_hyp_sent[1:-1],
score=cand_new_hyp_score))
else:
new_hypotheses.append(new_hyp_sent)
live_hyp_ids.append(prev_hyp_id) # 在序列中添加这个词
new_hyp_scores.append(cand_new_hyp_score)
if len(completed_hypotheses) == beam_size:
break
# 更新 state 和 o_prev
live_hyp_ids = torch.tensor(live_hyp_ids, dtype=torch.long, device=self.device)
h_tm1 = (h_t[live_hyp_ids], cell_t[live_hyp_ids])
att_tm1 = att_t[live_hyp_ids]
hypotheses = new_hypotheses
hyp_scores = torch.tensor(new_hyp_scores, dtype=torch.float, device=self.device)
if len(completed_hypotheses) == 0:
completed_hypotheses.append(Hypothesis(value=hypotheses[0][1:],
score=hyp_scores[0].item()))
completed_hypotheses.sort(key=lambda hyp: hyp.score, reverse=True)
return completed_hypotheses
训练
此次翻译任务,源语言是印第安人的语言 Cherokee,现在只有 2000 人使用,所以训练数据也很小,只有 20k 的平行语料库:

最后 BLEU 为 13.34
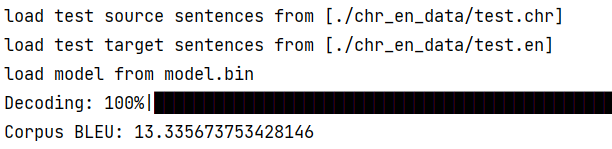
效果还算可以